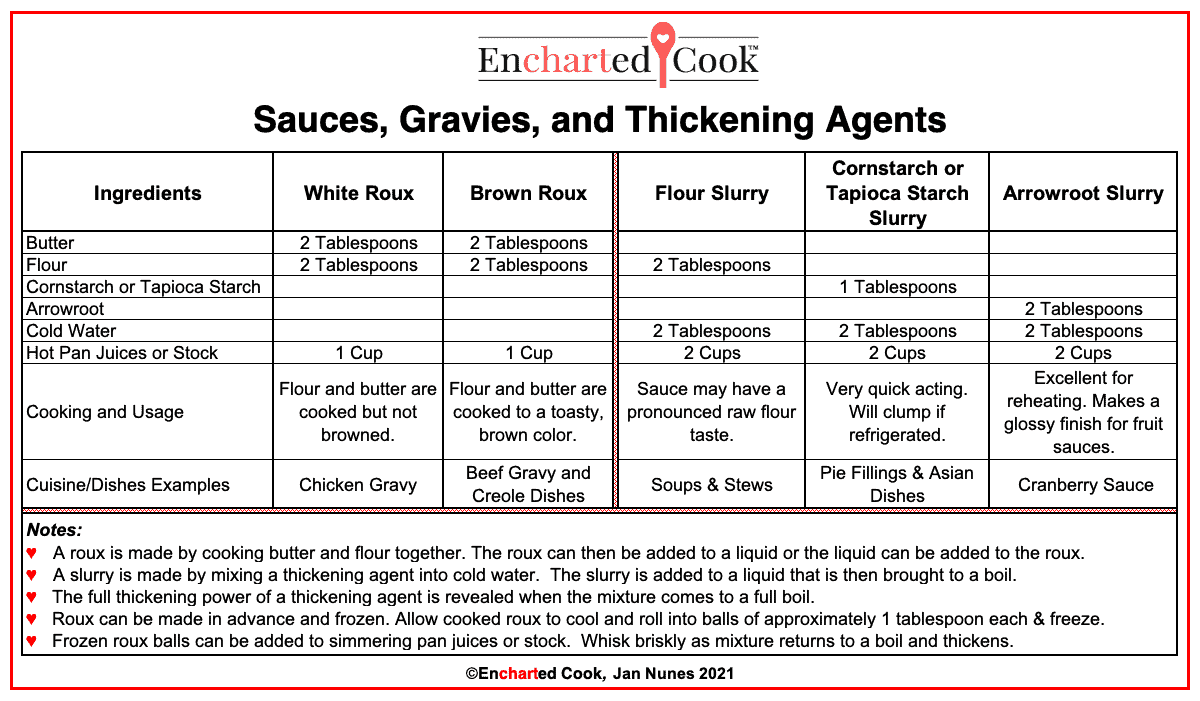
This is a quick reference chart of how to make roux-based gravies and sauces thickened by a slurry. It includes the full recipes and examples of the types of dishes for which each thickening agent is well suited.
Jump to:
There are four basic methods to create a sauce or a gravy. The use of a roux, the use of a slurry, the reduction of a liquid, and the creation of an emulsion. Both a roux and a slurry rely on the use of a thickening agent. This is a discussion on the use of thickening agents to create a sauce or gravy.
Thickening Agents
The most common thickening agents are flour, cornstarch, tapioca starch, and arrowroot. Each of these is well suited for particular uses.
Flour is used in making a roux and works well for meat-based gravies and milk gravies. While cornstarch, tapioca, and arrowroot are each used in making a slurry and are good choices for sauces that are fruit-based or may contain high acidity.
A roux is cooked. It is flour and fat cooked before it is used to thicken a liquid.
A slurry is not cooked. It is a thickening agent that is mixed into cold water that is then added to thicken a liquid.
How to Make a Roux
A roux is made by melting butter in a pan and then adding an equal amount of flour. The butter and flour are cooked together over low to medium-low heat until the desired color of the roux is achieved. The purpose of cooking the flour with butter is to eliminate the flavor of uncooked flour. Uncooked flour will overpower the flavor of any sauce or gravy. Fat drippings from roasted or cooked meats can also be used instead of or in addition to butter.
A white roux is cooked only until the flour has been cooked and generally retains a light color but it may become slightly darker, which will impart a nutty aroma and taste to the sauce or gravy.
A brown roux requires a longer cooking time and the goal is to achieve a richer flavor. The aroma and color will become a rich brown, but should not be black.
Care must be taken not to cook any roux too fast which may cause it to burn. A burnt roux will make a bitter unpleasant gravy.
Liquids like broths and stocks are whisked into a roux to make a gravy or sauce. The liquid is then brought to a simmer, which will result in a thickened gravy or sauce.
A roux-based gravy is an excellent accompaniment for meats.
How to Make a Slurry
A slurry is made when cold water is mixed well into a thickening agent. The slurry is then whisked into a liquid and cooked to create a sauce or gravy. If a slurry is added to a hot liquid the sauce will thicken almost instantly.
The best thickening agents for slurries are cornstarch, tapioca starch, and arrowroot. Flour can be used in a slurry, but there will always be an uncooked flour taste to the resulting gravy or sauce. It is included in this discussion as a possible slurry thickening agent, but the flavor is less desirable.
Arrowroot, in particular, gives a lovely, gleaming look to thickened fruits and compotes. It refrigerates and reheats well without clumping. However, it can give an unappetizing "slick" look to meat gravies and is not recommended for that purpose.
Slurries are excellent choices for making sauces for creamed vegetables, Asian-inspired dishes, thickened fruit fillings, compotes, and relishes.
Sauce and Gravy Quick Facts
- A roux is made by cooking butter and flour together. The roux can then be added to a liquid, or the liquid can be added to the roux.
- A slurry is made by mixing a thickening agent into cold water. The slurry is added to a liquid that is then brought to a boil.
- The full thickening power of a thickening agent is revealed when the mixture comes to a full boil.
- Roux can be made in advance and frozen. Allow the cooked roux to cool and roll into balls of approximately 1 tablespoon each & freeze.
- Frozen roux balls can be added to simmering pan juices or stock. Whisk briskly as the mixture returns to a boil and thickens.
- Slurries make sauces and gravies quickly, while a roux-based gravy or sauce will take more time to prepare.
- Butter is simply stated for making a roux, however any fat or drippings from cooking or roasting meats can also be used.
Related Posts
- Leavening Agents & Methods Chart
- Basic Cake Recipes Chart
- Simple Syrup Recipes Chart
- Quick Bread Recipes Chart






Comments
No Comments